Cognition
Servings:
Third-Party Testing
We believe trust is earned through transparency. That’s why we provide full access to our third-party test results, so you can feel confident in what you’re taking. View all third-party tests.
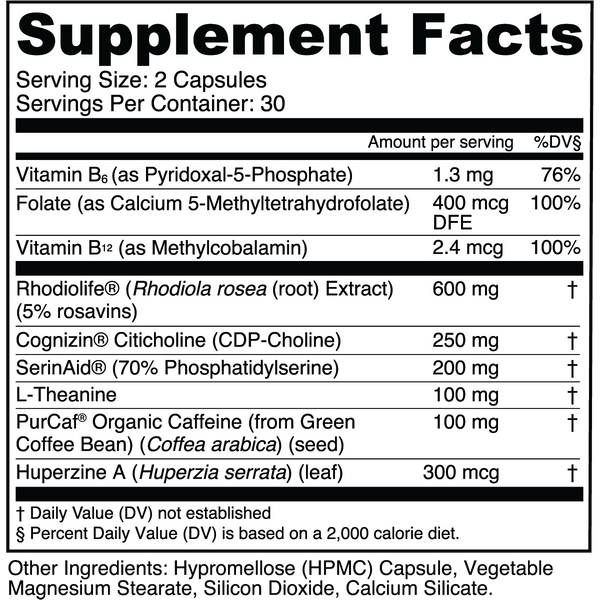
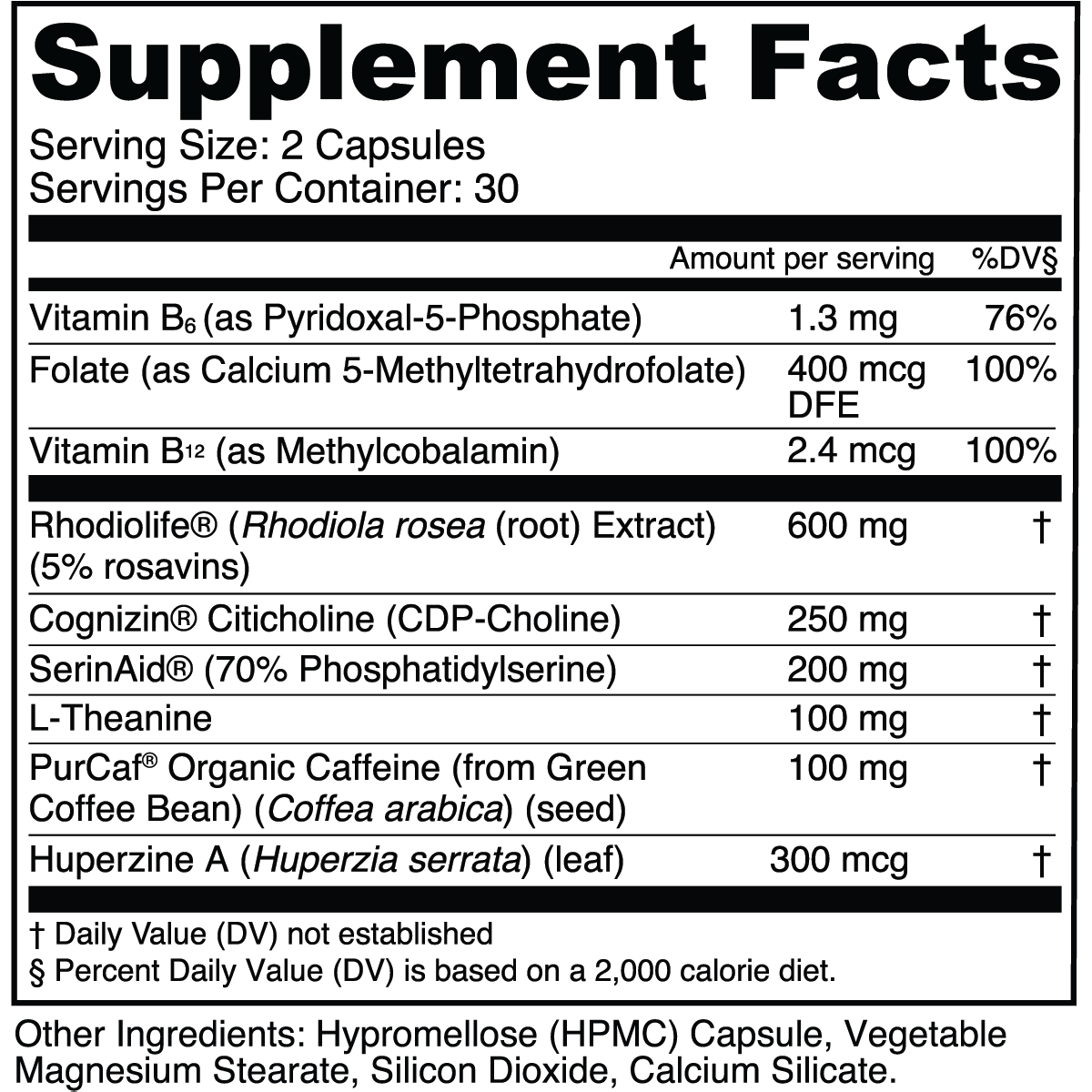
Transparent Labs Cognition is a high-performance, evidence-based nootropic supplement featuring four key ingredients that support healthy cognitive function: Rhodiolife® (Rhodiola rosea extract), Cognizin® (citicoline), SerinAid® (phosphatidylserine), and PurCaf® (organic caffeine).
This formula also contains B vitamins, L-theanine, and huperzine-A to complement overall brain health.
Our Cognition supplement includes patented and proven ingredients tested in human clinical trials for improving cognitive performance (e.g., working memory and mental alertness), brain function, stress resilience, mood, and more!
And with just the right amount of caffeine, Cognition helps you dial in and focus without feeling overstimulated or jittery.
Orders in the US over $99 ship free.
Once your order has shipped out from our fulfillment center, you will receive a Shipping Confirmation email. If you selected a tracked shipping method, you will receive your tracking information, along with the necessary steps to track your order, within this email. Please note, orders are generally fulfilled same day or next business day.
Click here for the full shipping and delivery guide »
45 Day Satisfaction Guarantee
If you are not satisfied with your product, we will offer you a full refund or store credit for the value of the item within 45 days of delivery.
Click here for the full refund policy »
why use Cognition?
A clinically researched nootropic blend formulated to boost cognitive performance, sharpen memory, and improve stress response without overstimulation.
Sharpens Memory & Focus
Promotes neurotransmitter production for improved mental clarity, memory recall, and overall cognitive function.

Reduces Stress & Enhances Mood
Contains adaptogens and phosphatidylserine to regulate cortisol, elevate mood, and support emotional resilience.

Sustained Mental Energy
Balanced combination oPurCaf® organic caffeine and L-theanine provides smooth, focused alertness without jitters.

Supports Long-Term Brain Health
Premium ingredients protect and nourish neurons, supporting cognitive function and overall neurological health.

Key Ingredients
Rhodiolife® (Rhodiola rosea Root Extract, 5% Rosavins)
600 mg
Rhodiolife® is the world’s first standardized Rhodiola rosea extract to be made commercially available. This patented ingredient is developed by Nektium Pharma and is 100% identity guaranteed, ensuring authenticity and potency with 5% rosavins and 1.8% salidroside (the key beneficial constituents in Rhodiola).

Cognizin® Citicoline (CDP-Choline)
250 mg
Cognizin® is a patented form of choline known as citicoline, or cytidine diphosphate (CDP)-choline, the industry’s gold standard for choline supplementation.

SerinAid® (70% Phosphatidylserine)
200 mg
SerinAid® is the purest and most potent phosphatidylserine ingredient on the market, derived exclusively from plant sources.

PurCaf® Organic Caffeine (from Green Coffee Bean)
100 mg
While many nootropic supplements contain synthetic caffeine, we formulated Cognition with organic caffeine derived from green coffee beans (as PurCaf®).