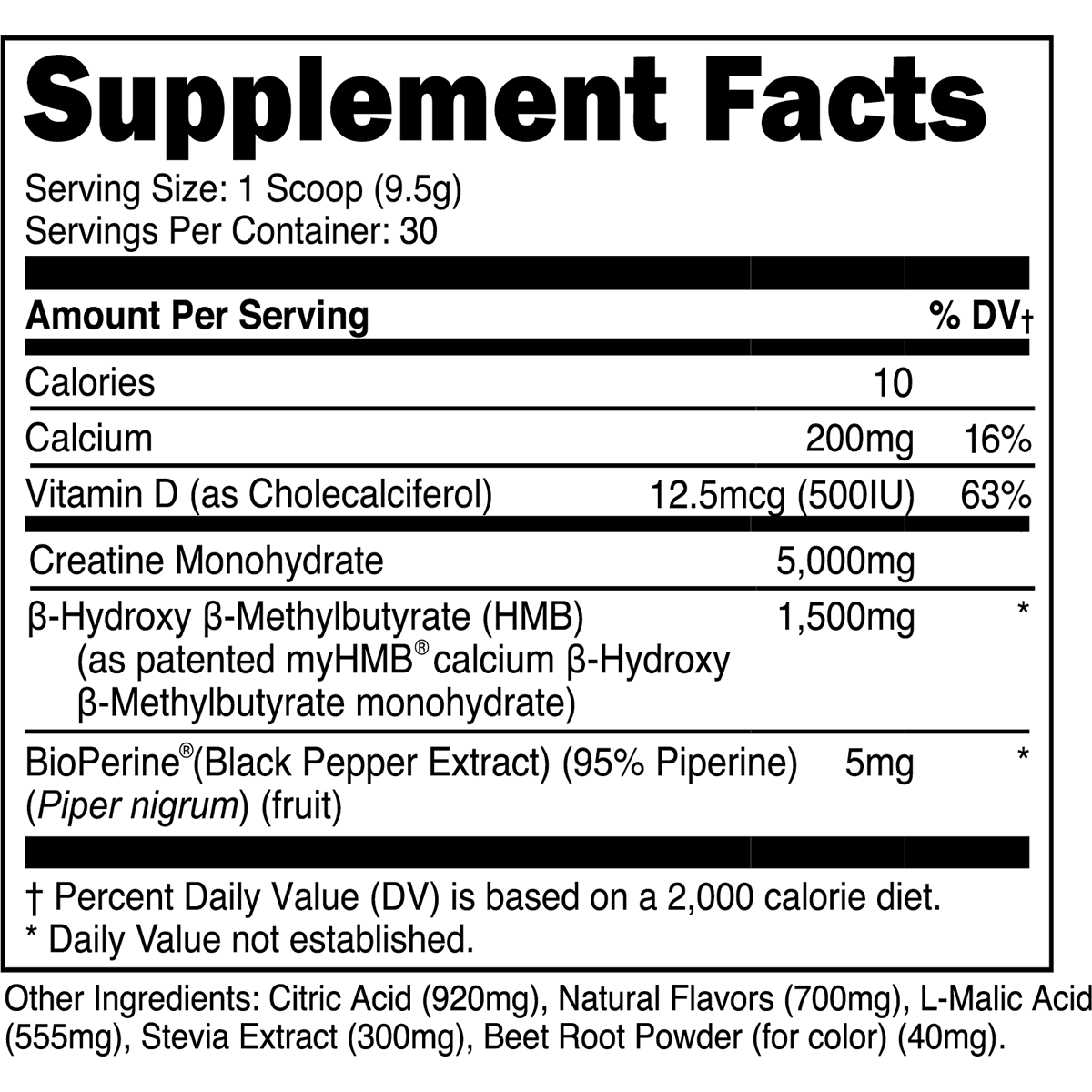
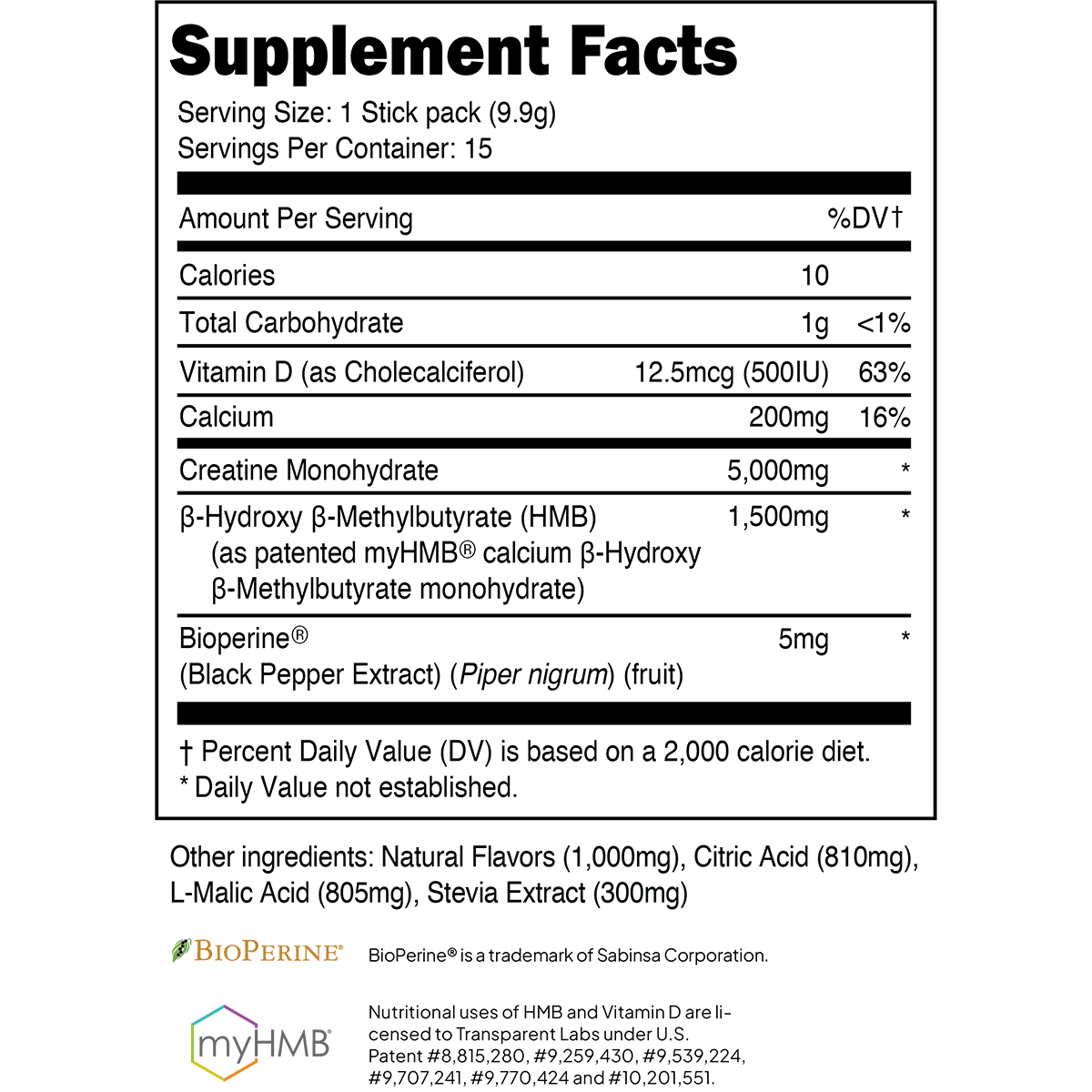
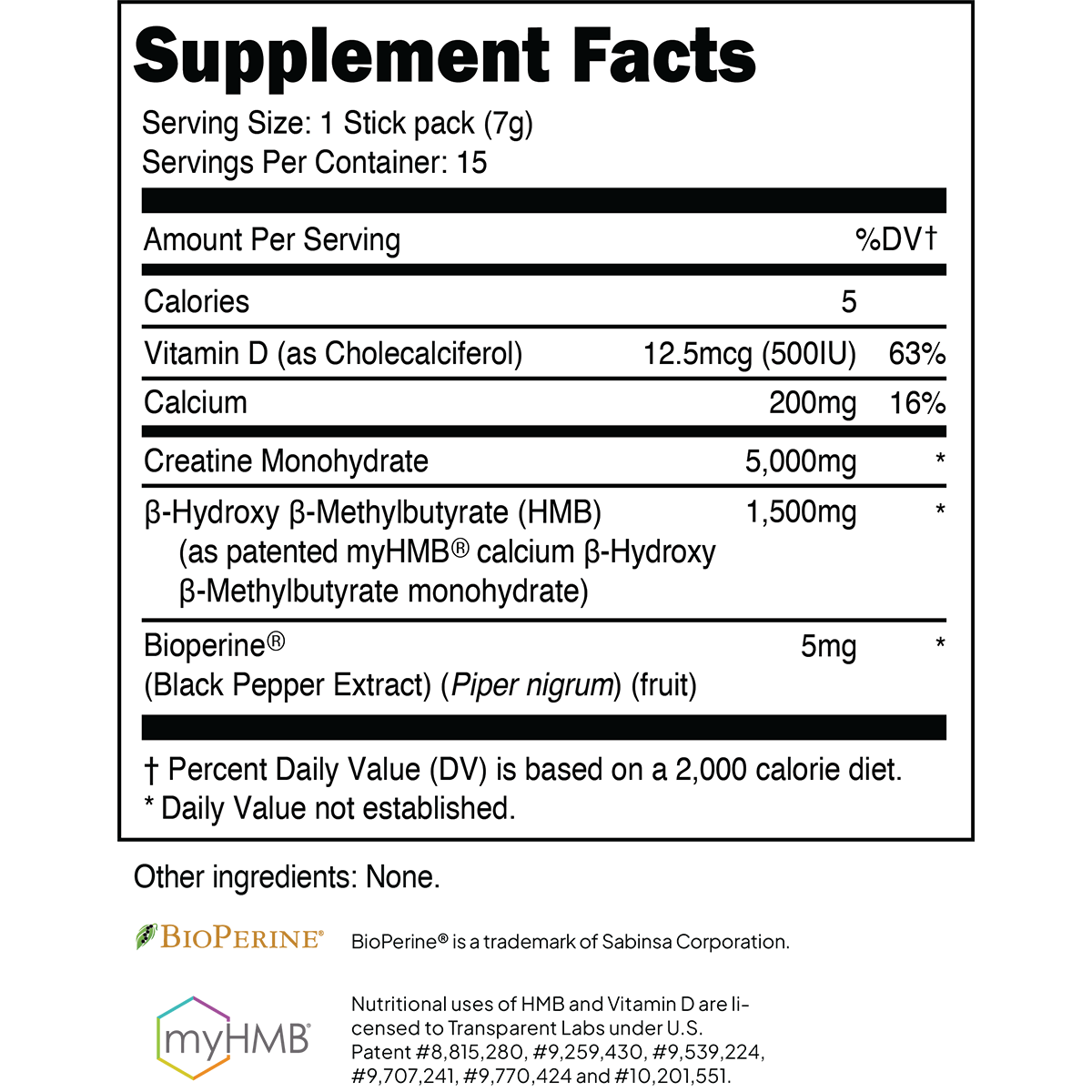
Athletes and gym-goers are constantly looking to gain an "edge" by taking dietary supplements with purported muscle-building effects. Sadly, a majority of the supplements marketed for such purposes contain few, if any, ingredients backed by empirical data.
The good news is that a handful of evidence-based supplement ingredients can directly promote muscle hypertrophy and/or reduce muscle protein breakdown. A few supplements can also support muscle growth through indirect mechanisms, such as improving muscle strength and enhancing testosterone levels.
This article provides an overview of six evidence-based muscle-building supplements to consider adding to your regimen and how to use them properly.
6 Evidence-Based Supplements for Promoting Muscle Growth
1. Protein Powder (e.g. Whey Protein Isolate)
Protein is integral to the processes of muscle repair and hypertrophy. Although whole foods should account for the majority of your total protein intake, protein powders are an effective and practical way to make sure you hit your daily protein intake goals.
Furthermore, taking a quality whey protein powder, such as Transparent Labs 100% Grass-Fed Whey Protein Isolate, after working out is one of the best ways to kickstart recovery and stimulate muscle protein synthesis [1]. This is especially true for active gym-goers and athletes who require higher amounts of protein to maintain and build muscle tissue.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Supplemental Protein
-
Convenient Source of High-Quality Protein: Protein powders, particularly those with complete protein sources (e.g., whey protein isolate), are generally easy to digest and provide a comprehensive amino acid profile to maximize muscle protein synthesis [2]. Any "complete" protein source contains a sufficient balance of all nine essential amino acids.
-
Support Lean Muscle Mass: Consistently hitting your protein intake goals sets the foundation for improving body composition and increasing muscle mass, and this is where protein powders come in handy [3].
How to Use Protein Powder
As a general rule of thumb, consuming at least 20-30 grams of protein powder—preferably whey protein—post-exercise will optimize muscle protein synthesis [4]. (Most protein supplements provide 20-25 grams of protein per serving.)
Total protein intake should be around 0.7-1.1 grams of protein per pound of body weight per day [5]; this range will suffice for most active individuals aiming to increase muscle mass. Additionally, evenly distributing protein intake across 3-5 meals throughout the day can further bolster muscle growth [6].
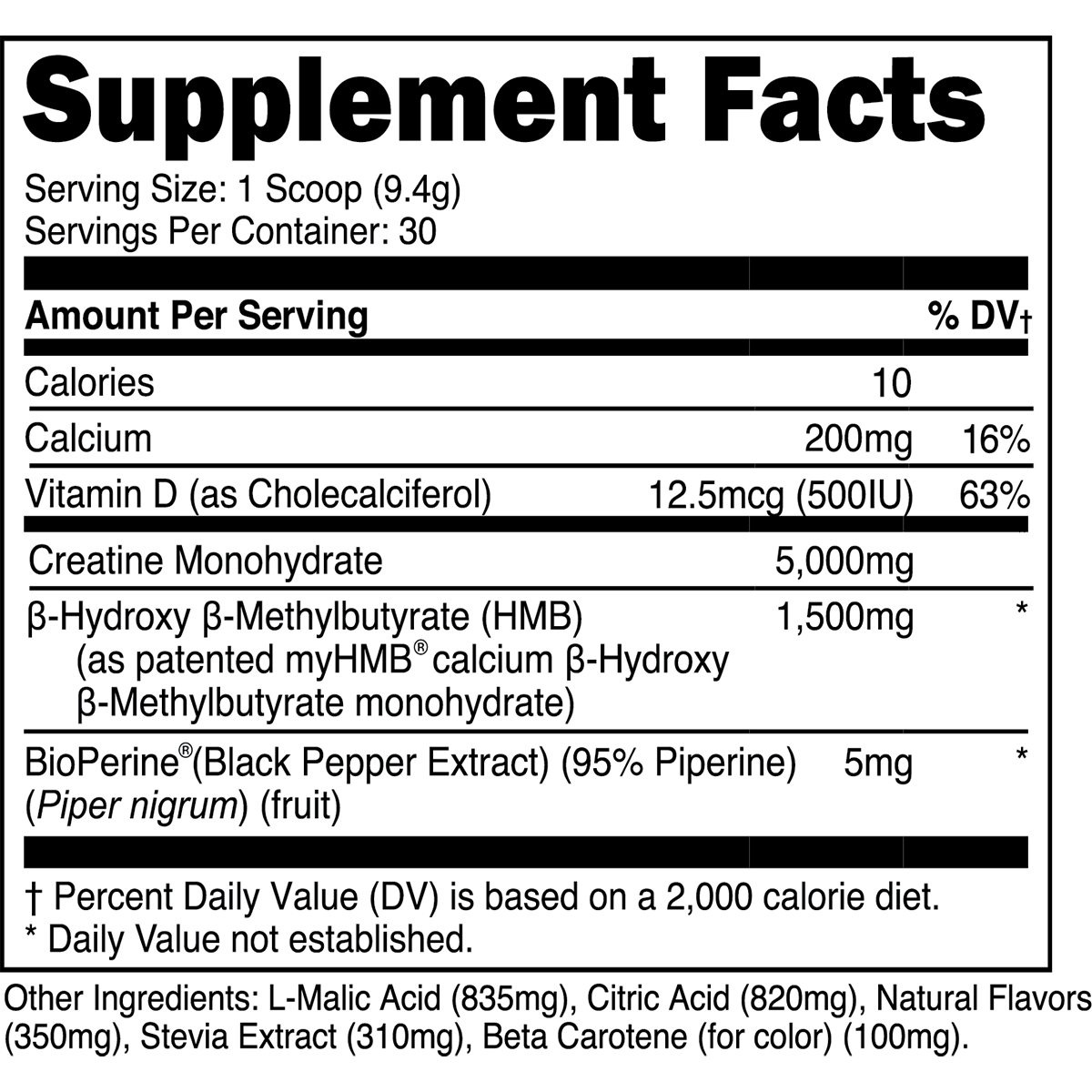
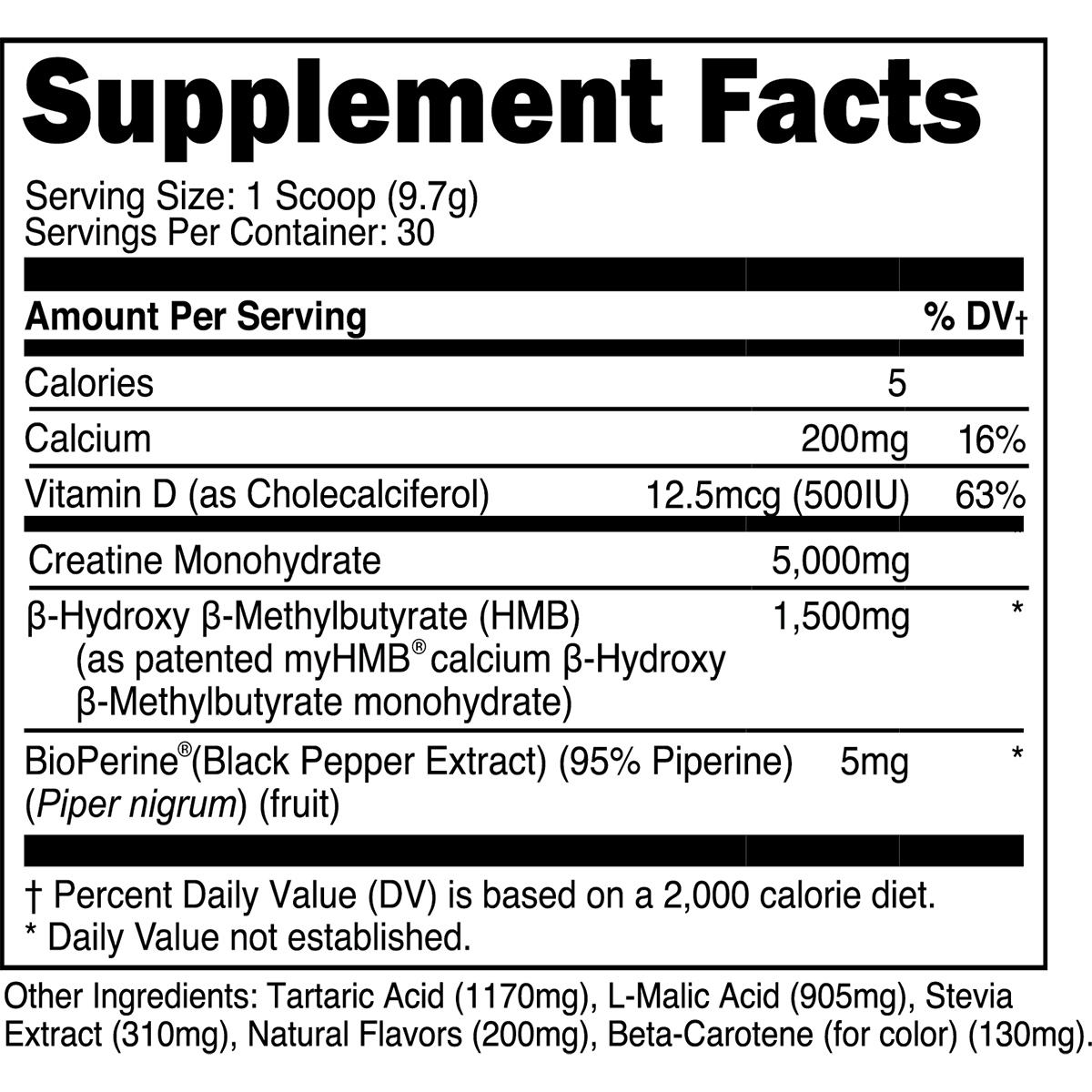
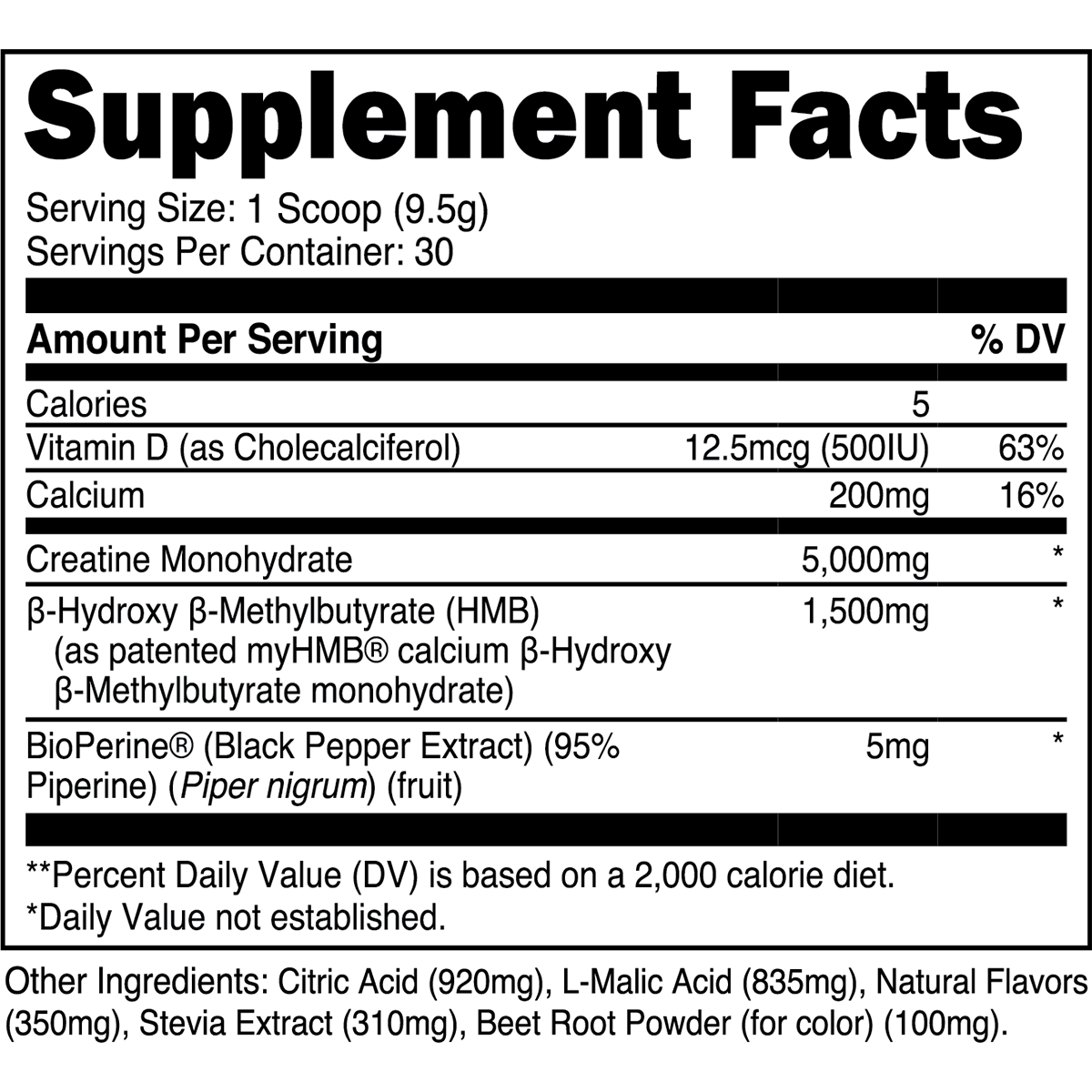
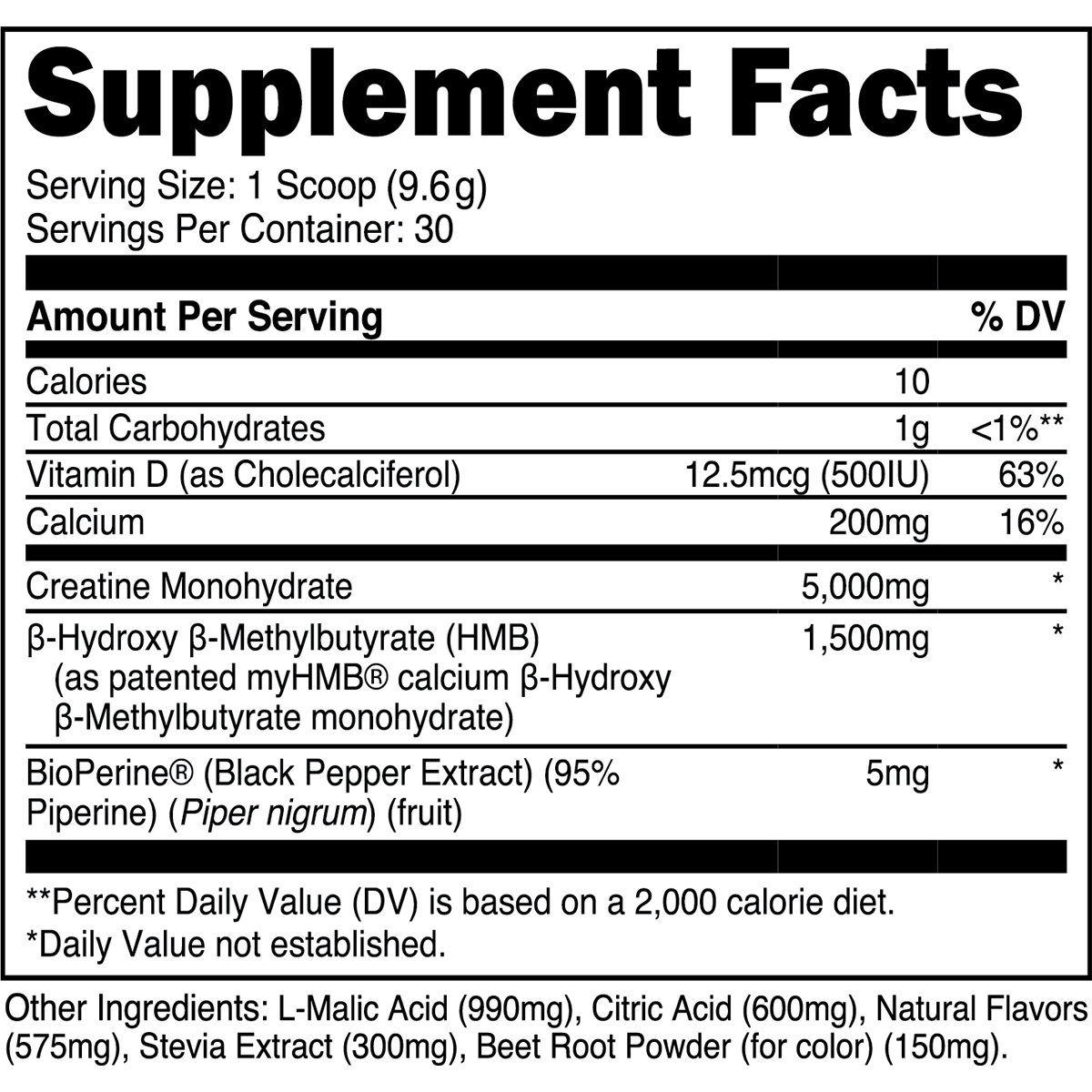
2. Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate is the most studied sports supplement (literally), followed closely by everyone's favorite stimulant, caffeine. In brief, creatine supplements bolster phosphocreatine reserves within muscle cells, thereby facilitating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production during high-intensity exercise.

Evidence-Based Benefits of Creatine Monohydrate
-
Enhanced Muscular Strength and Power: Supplementation with creatine is demonstrated to bolster strength and power output, translating to more effective workouts [7].
-
Accelerated Recovery: Supplementing with creatine monohydrate can expedite intra- and inter-workout recovery, thereby mitigating performance decrements from muscle soreness [8].
-
Increase Muscle Mass: Creatine supplementation is suggested to promote muscle growth through several mechanisms, albeit creatine is not likely to produce anabolic effects on its own [9].
How to Use Creatine Monohydrate
In a pivotal "loading vs. maintenance dose" study, muscle creatine stores were virtually identical (~ 20% increase) between subjects consuming just 3 grams of creatine monohydrate per day for 28 days and those consuming a much larger 20 grams per day for six days [10]. Thus, taking ~3-5 grams of creatine monohydrate daily for at least four weeks will produce similar skeletal muscle creatine increases as an aggressive creatine loading phase.
3. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) and Essential Amino Acids (EAAs)
Essential amino acids (EAAs) are a group of nine amino acids, which includes the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), that we must consume for proper biological function and protein synthesis. BCAAs are a subset of three EAAs—L-leucine, L-isoleucine, and L-valine—that are considered "master regulators" of muscle protein synthesis [11].
Hence, EAAs and BCAAs have become popular supplements for active individuals looking to improve recovery and support muscle growth.
Evidence-Based Benefits of EAAs and BCAAs
-
Stimulate Muscle Protein Synthesis: EAAs, notably the BCAAs, activate the mechanistic/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, which is a key mediator of muscle hypertrophy. As little as 7-10 grams of EAAs (in a proper ratio) can stimulate a robust response in muscle protein synthesis [12].
-
Alleviate Muscle Soreness: Supplementation with BCAAs has been demonstrated to lessen exercise-induced muscle damage and subsequent soreness, thereby enhancing recovery [13].
-
Reduce Muscle Protein Breakdown: Beyond stimulating muscle protein synthesis, EAAs/BCAAs have been shown to attenuate muscle protein breakdown (MPB)[14]. As such, supplementing with BCAAs/EAAs can help preserve lean muscle mass on a calorie-restricted diet and during strenuous training sessions.
How to Use EAAs and BCAAs
BCAAs/EAAs are typically taken before, during, or after working out or sporting events. A standard dose of BCAAs/EAAs ranges from 5 to 10 grams, with adjustments made according to individual requirements and the intensity of the workout.
4. Beta-Alanine
Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid that bonds with histidine to form an endogenous dipeptide called carnosine. This dipeptide helps buffer against the acidic byproducts of intense muscle exertions, thereby delaying fatigue. Carnosine synthesis is limited by beta-alanine availability; hence, supplementing with beta-alanine can improve exercise performance by increasing muscle carnosine levels. Over time, this enhanced training capacity can lead to greater muscle hypertrophy.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Beta-Alanine Supplementation
-
Improved Endurance/Resistance to Fatigue: Beta-alanine supplementation enhances muscle buffering capacity, which delays the onset of muscular fatigue during high-intensity exercise [15]. This ergogenic effect is particularly beneficial for athletes engaged in sports requiring repeated bouts of high-intensity efforts, such as sprinting or competitive rowing.
-
Increased Lean Body Mass: By allowing yourself to train harder, longer, and more effectively, beta-alanine supplementation can contribute to muscle growth [16].
How to Use Beta-Alanine
The effective dosage of beta-alanine is 4-6 grams per day, typically divided into smaller doses to minimize the tingling sensation (paresthesia) that some people experience in the initial days of use [17]. This dosage regimen can increase muscle carnosine concentrations by as much as 80% within 10 weeks [18].
5. Phosphatidic Acid
Phosphatidic acid (PA) is a naturally occurring phospholipid that functions as a signaling molecule in the mechanical activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, which, as mentioned earlier, mediates muscle protein synthesis [19]. Supplemental phosphatidic acid is also posited to promote mTOR signaling through a distinct extracellular pathway that ultimately converges with mechanical stimuli (e.g. resistance training), thereby producing an effectual muscle hypertrophy response [20].

Evidence-Based Benefits of Phosphatidic Acid Supplementation
-
Enhances muscle protein synthesis by activating the mTOR signaling pathway [21]
-
Improves muscle hypertrophy and strength when combined with resistance training [22].
How to Use Phosphatidic Acid
An evidence-based daily dose of phosphatidic acid ranges from 500 mg to 750 mg. Each serving of Transparent Labs GROWTH provides 750 mg of patented Mediator® Phosphatidic Acid to ensure high quality and consistency (which can be hit or miss with generic formulations).
6. Eurycoma longifolia (Tongkat Ali/Longjack)
Eurycoma longifolia, commonly referred to as Tongkat Ali or Longjack, has been used in Eastern medicine for its various health benefits, including its purported effects on physical performance and muscle growth. The bioactive compounds in Eurycoma longifolia, such as eurypeptides, quassinoids, and glycosaponins, appear to modulate testosterone and estrogen production, thereby influencing muscle hypertrophy and strength.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Eurycoma longifolia Supplementation
-
Increase testosterone levels: Multiple studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Eurycoma longifolia supplementation for enhancing testosterone levels, which is a critical anabolic hormone for muscle protein synthesis and overall muscle growth [23].
-
Improve athletic performance: By reducing fatigue and increasing energy levels, Eurycoma longifolia supplementation can enhance exercise capacity (which can also promote muscle growth over time) [24, 25].
-
Balance Stress Levels and Inflammation: The adaptogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties of Eurycoma longifolia can indirectly improve muscle recovery following intense physical activities by balancing cortisol levels and reducing oxidative stress [26, 27].
How to Use Eurycoma longifolia
The appropriate dosage of Tongkat ali extract depends on several factors, including age, health status, and reasons for taking the supplement. Most clinical studies have used dosages ranging from 200 to 600 mg daily for 8-12 weeks.
If you're using Transparent Labs LJ100®, 100 to 300 mg per day is plenty, as it contains a 100:1 extract of Eurycoma longifolia.
Muscle-Building Checklist
Even the best supplements for muscle growth can only take your results so far. Before spending tons of money on dietary supplements, focus on the following:
-
Diet and Nutrition: Supplements work best when integrated into a well-rounded diet. Ensure you're consuming enough calories and macronutrients to support muscle growth. Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, also play a crucial role in overall health and performance.
-
Training Program: Following a diligent resistance-training routine is imperative for optimal results when taking supplements for muscle growth. If you're unsure where to start, a Push-Pull-Legs program is tough to beat.
-
Rest and Recovery: Muscles grow when we rest, not during workouts. Adequate sleep and rest days are essential for recovery and muscle hypertrophy. Overtraining or under-resting can negate the benefits of even the best supplements for muscle growth.
-
Hydration: Staying hydrated is vital for overall health and performance. Water is involved in numerous bodily functions, including nutrient transport and muscle contraction. Dehydration can impair muscle recovery and performance.
-
Consistency and Patience: Building muscle is a gradual process. Consistency in training, nutrition, and supplementation sets a foundation for long-term success. It's important to have realistic expectations and understand that making small steps in the right direction from one day to the next will eventually pay off.
Key Takeaway
Protein powders, BCAAs/EAAs, creatine monohydrate, beta-alanine, phosphatidic acid, and Eurycoma longifolia can benefit just about anyone looking to build muscle mass. However, using these supplements in lieu of a proper diet and training routine will lead to underwhelming results. Make sure you're leading a healthy lifestyle and consistent with your workouts to maximize the muscle-building potential of the supplements discussed herein.
Lastly, consumers should purchase supplements from reputable sources to ensure that product quality and potency claims are met. Label transparency and third-party testing are indicators of trustworthy supplement brands. Click here to learn more about how Transparent Labs is setting the trend for premium, evidence-based supplements.