Hydrate
Size:
10 Flavors Available:
Third-Party Testing
We believe trust is earned through transparency. That’s why we provide full access to our third-party test results, so you can feel confident in what you’re taking. View all third-party tests.

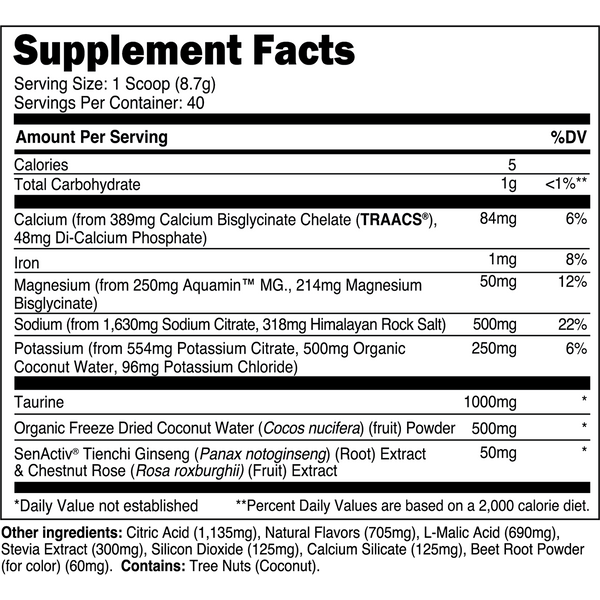
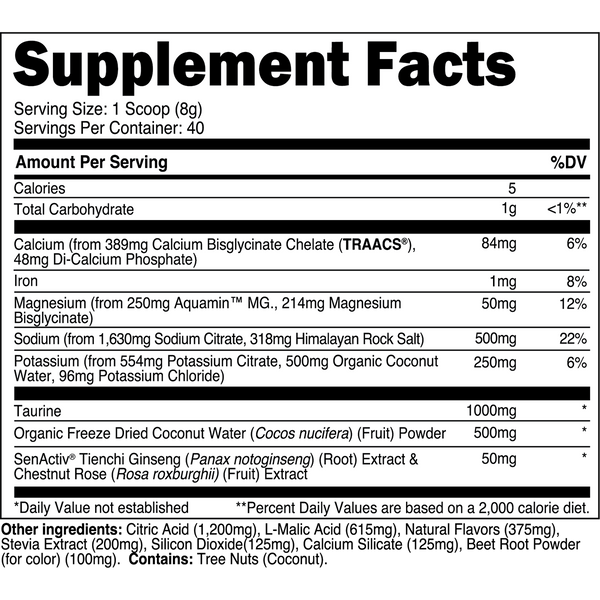
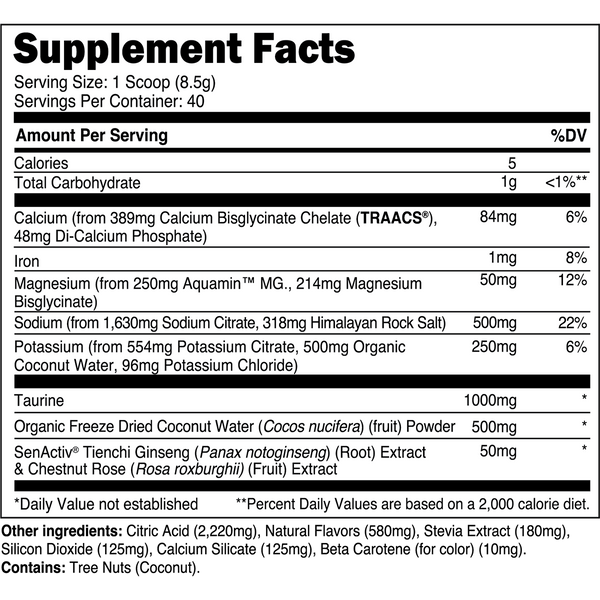
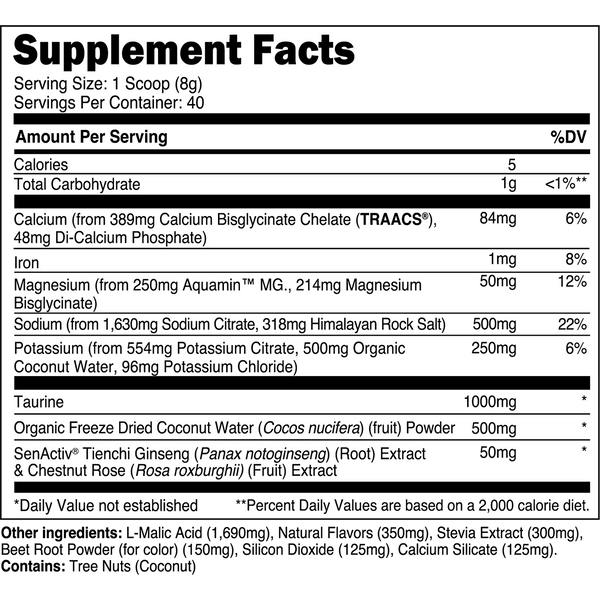
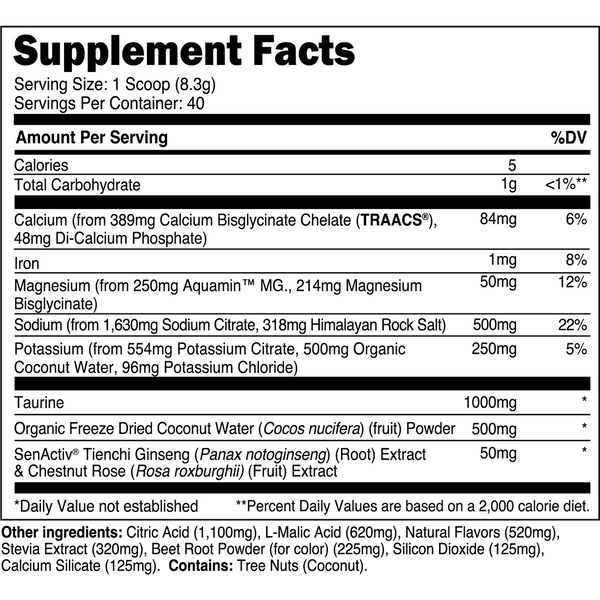
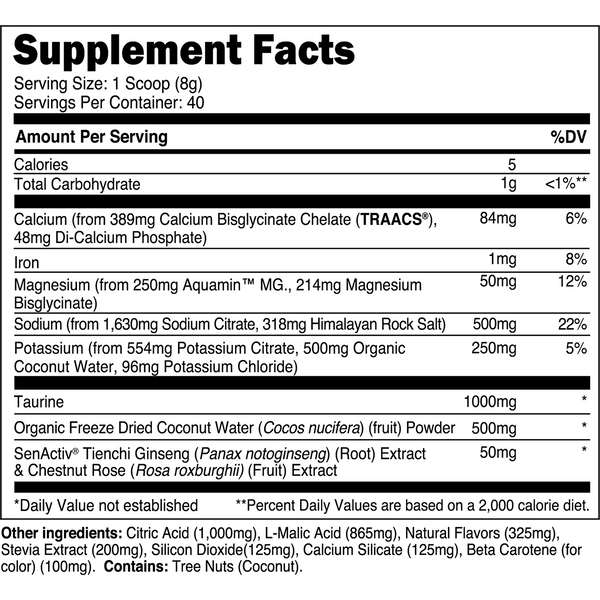
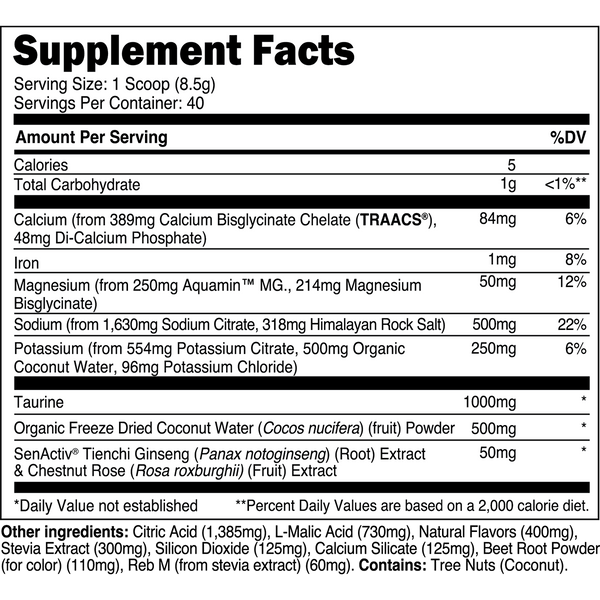
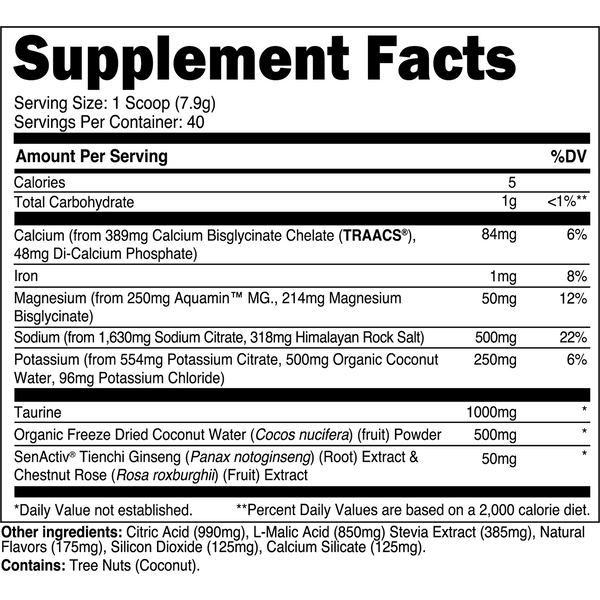
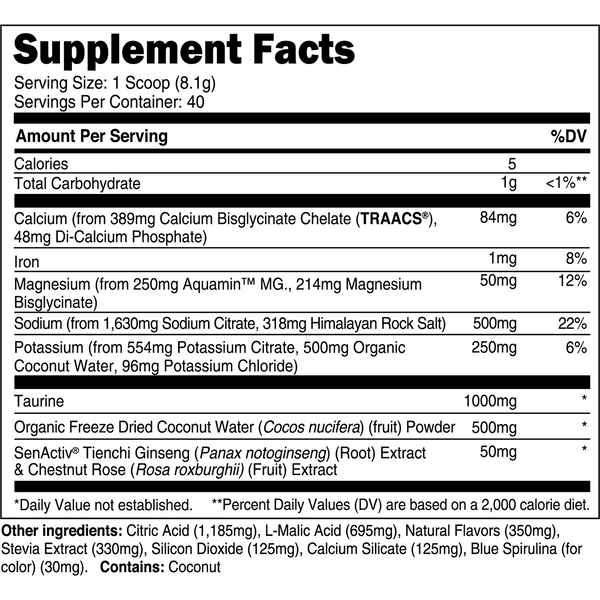
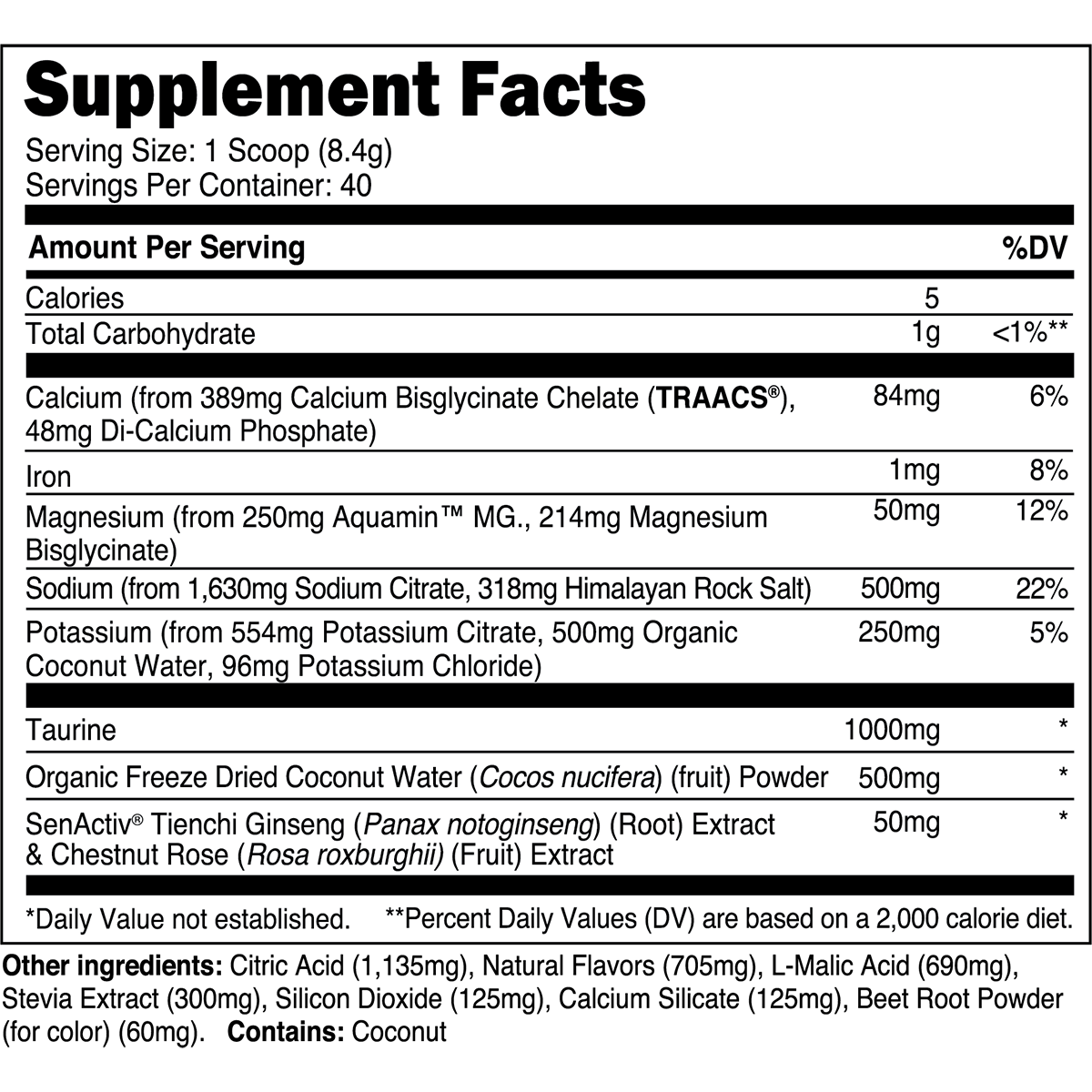
Transparent Labs Hydrate is a sugar-free electrolyte powder featuring bioavailable minerals, taurine, SenActiv®, and coconut water powder to help you stay hydrated throughout the day and during training. Unlike conventional “sports nutrition drinks” and many electrolyte powders, Transparent Labs Hydrate contains no added sugars, artificial coloring, or artificial sweeteners.
Instead, this electrolyte supplement is made with natural flavors and sweetened with stevia to deliver a refreshing, sugar-free hydration boost to your daily water intake.

















Orders in the US over $99 ship free.
Once your order has shipped out from our fulfillment center, you will receive a Shipping Confirmation email. If you selected a tracked shipping method, you will receive your tracking information, along with the necessary steps to track your order, within this email. Please note, orders are generally fulfilled same day or next business day.
Click here for the full shipping and delivery guide »
45 Day Satisfaction Guarantee
If you are not satisfied with your product, we will offer you a full refund or store credit for the value of the item within 45 days of delivery.
Click here for the full refund policy »
why use Hydrate?
Stay hydrated and on top of your game every day with essential electrolytes, and natural performance-boostersSenActiv™, and taurine, ensuring your body is efficiently replacing electrolytes lost through sweat and activity.
Optimize Hydration
Transparent Labs Hydrate contains bioavailable electrolytes to keep your cells hydrated, while helping to regulate fluid balance and prevent excessive fluid retention.

Promote Muscle Recovery
Transparent Labs Hydrate includes adaptogens and taurine to support recovery from physical activity.

Support Muscle Function
Replenish electrolytes to support muscle function and avoid cramps during exercise.

Enhance Athletic Performance
Adequate Hydration sets the foundation for athletes and active individuals to perform their best, whether you're engaging in moderate exercise or intense training.

Key Ingredients
SenActiv™
50 mg
SenActiv® is a patented adaptogenic complex that helps accelerate muscle recovery during/after strenuous exercise.

Taurine
1,000 mg
Taurine is a sulfur-containing amino acid with numerous performance enhancing properties.

Calcium (as TRAACS® Calcium Bisglycinate and Di-Calcium Phosphate)
84 mg
Calcium is a crucial micronutrient that associates with mitochondria in muscle cells to stimulate ATP (energy) synthesis.

Magnesium (as Aquamin™ Mg)
50 mg
Magnesium is a vital electrolyte mineral that has numerous roles in the body, one of which is regulating muscle contraction.